Description
Gas Bank & Pipe Line – Safe, Reliable, and Efficient Gas Distribution System
Introduction to Gas Bank & Pipe Line
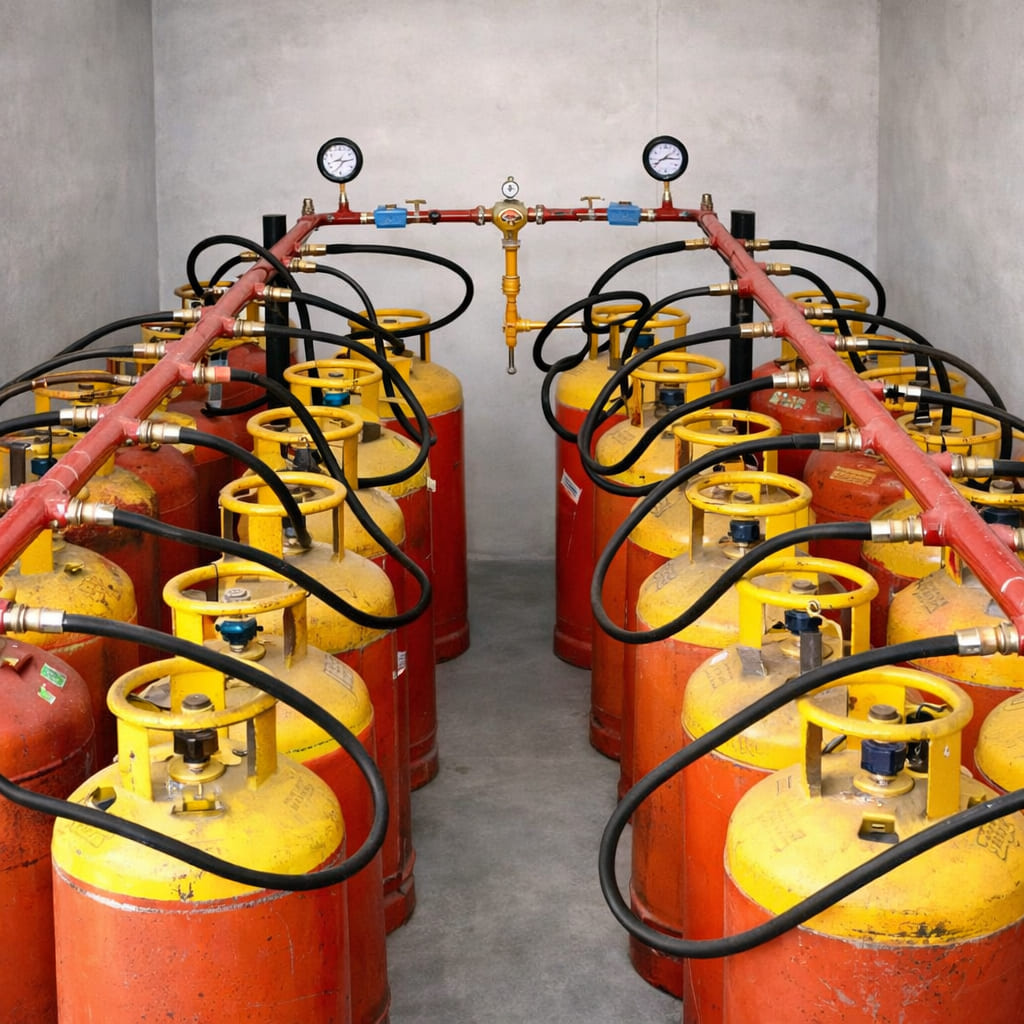
A Gas Bank & Pipe Line system is one of the most reliable methods of ensuring a continuous and safe gas supply across industries, healthcare facilities, and research laboratories. Instead of relying on single cylinders, which can cause interruptions and safety concerns, gas banks are designed to connect multiple cylinders in a centralized system. Through carefully engineered pipelines, gas is distributed seamlessly to different areas of use. This setup not only improves safety but also boosts operational efficiency, making it a vital installation for organizations that require an uninterrupted gas flow.
Why Gas Bank Systems Are Essential
Gas is a critical resource in medical, industrial, and research applications. In hospitals, medical oxygen needs to flow without interruption to critical care units, while in industries, gases like nitrogen, argon, or acetylene play an important role in manufacturing processes. A gas bank system ensures that there is always a backup supply ready when one cylinder is empty, preventing downtime and safeguarding operations. The connected pipeline network delivers gas at the right pressure and volume, making it both efficient and dependable.
Components of a Gas Bank & Pipe Line System
To understand its efficiency, it’s important to know the core components:
-
Gas Cylinders: The primary storage units containing the required gases.
-
Cylinder Manifold: A structure that interconnects multiple cylinders, ensuring simultaneous supply.
-
Pipeline Network: Durable pipes that transport gas to the designated points of use.
-
Pressure Regulators: Devices that control and maintain safe gas pressure.
-
Valves and Safety Devices: Critical for controlling flow, preventing leaks, and ensuring user safety.
Each component is designed to meet stringent safety standards, making the entire system highly secure and reliable.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of a Gas Bank & Pipe Line system makes it suitable for a wide range of industries and institutions:
-
Healthcare & Hospitals: Continuous oxygen supply for ICUs, operation theaters, and wards.
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: Gas flow for research, production, and testing.
-
Manufacturing Units: Welding, cutting, and metal fabrication processes.
-
Laboratories & Research Centers: Safe and accurate delivery of gases for experiments.
-
Food & Beverage Industry: Controlled use of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and other gases.
This adaptability highlights why gas banks and pipeline systems are preferred over standalone cylinders.
Safety and Reliability – The Top Priority
When dealing with gases, safety is paramount. A gas bank system minimizes risks associated with handling individual cylinders, as they remain securely connected in a controlled setup. Pipelines reduce the need for manual cylinder shifting, preventing accidents and ensuring smoother operations. Safety features like non-return valves, flashback arrestors, and pressure regulators add multiple layers of protection, ensuring absolute reliability.
Advantages of Installing a Gas Bank & Pipe Line
Implementing such a system brings numerous benefits:
-
Uninterrupted Gas Supply – Eliminates downtime by automatic switching between cylinders.
-
Operational Efficiency – Centralized control allows easy monitoring and maintenance.
-
Cost-Effective – Reduces wastage and lowers operational costs compared to individual cylinders.
-
Enhanced Safety – Secure cylinder arrangement and high-quality pipelines reduce accident risks.
-
Scalability – Can be expanded to accommodate higher gas demands in the future.
Advanced Engineering and Design
Modern gas bank and pipeline systems are built with advanced engineering techniques, using corrosion-resistant materials and durable fittings. This ensures long-lasting performance even under high-pressure conditions. Computerized monitoring systems can also be integrated, allowing organizations to keep track of gas levels, pressure, and flow in real time. Such innovation adds convenience while improving efficiency.
Importance in Healthcare Infrastructure
In hospitals and medical institutions, a Gas Bank & Pipe Line is not just a convenience—it is a life-saving system. Medical gases such as oxygen, nitrous oxide, and compressed air are crucial for patient care. From operating theaters to neonatal ICUs, the pipeline ensures an uninterrupted gas supply, which can be the difference between life and death. The redundancy built into gas banks guarantees that medical staff can focus on patients without worrying about supply interruptions.
Maintenance and Regular Inspections(Gas Bank & Pipe Line)
For smooth functioning, regular inspections and maintenance are essential. Routine leak checks, valve testing, and pressure monitoring ensure that the system operates without flaws. Scheduled maintenance prevents breakdowns and extends the system’s lifespan, providing peace of mind for both healthcare institutions and industries.
Compliance with Standards(Gas Bank & Pipe Line)
Gas banks and pipeline systems are designed and installed in compliance with international safety standards. Certifications ensure that every component—from cylinders to regulators—is tested for durability and safety. This adherence to standards reassures organizations that their system is both safe and legally compliant.
Choosing the Right Gas Bank & Pipe Line Provider
Selecting a trusted manufacturer or supplier makes a significant difference in system quality. An expert provider will:
-
Assess the specific gas requirements.
-
Design a customized manifold and pipeline system.
-
Install the system with strict adherence to safety protocols.
-
Provide after-sales service and maintenance support.
This holistic approach ensures that clients receive a reliable, efficient, and safe solution.
Future of Gas Bank Systems
As technology evolves, so does the efficiency of gas distribution systems. Future innovations are expected to include smart sensors, digital monitoring dashboards, and automated cylinder replacement mechanisms. These advancements will further enhance safety, efficiency, and sustainability in gas supply infrastructure.
Conclusion
A Gas Bank & Pipe Line system is more than just a technical installation—it is the backbone of safe and reliable gas distribution across industries and healthcare facilities. By ensuring uninterrupted supply, enhancing safety, and improving efficiency, it empowers organizations to operate at their best. With proper design, installation, and maintenance, such a system becomes a long-term asset that supports critical operations with absolute dependability.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.